After a lot of time and research (about 48 hours to be exact) I have finally completed my biology final!!! I really hope you enjoy it and learn as much as I did. Throughout my research, I used several Internet sources as well as the book "Modern Biology". Below is a complete book source.
Postlethwait, John H and Janet L, Hopson "Modern Biology" Orlando, Austin, New York, San Diego, Toronto, London; Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 2006.
Enjoy and please leave a comment!
Saturday, June 5, 2010
#1 Water


Water is a well known polar molecule. So what exactly is a polar molecule? A polar molecule is a molecule that has a different charge in the chemical bonds. i.e. one part of the molecule would have a positive charge while the other would have a negative charge. Water contains one oxygen molecule which has a negative charge and two hydrogen molecules which have a positive charge. Above is a sketch of a water molecule.
Source: WWW.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/p/polarmol.html
#2 Phospholipid Bilayer



The phospholipid bilayer is made up or two layers of phospholipids. Phospholipids are made of two fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule. The biomolecule that is found in the phosopholipid bilayer is lipids' an organic molecule that cannot dissolve in water. Three types of lipids are neutral rats, phospholipids and cholesterol. Above is the structure of the phospholipid bilayer, chemical formula of a lipid, and bacon which contains a lot of lipids.
Source: WWW.wisc-online.com/object/vicwobjece/aspx
Pg 59 Modern Biology
#3 Phospholipid Bilayer
#4 Sugar

Sugar is found in the central vacuole of plants an it is made by photosynthesis. Sugars chemical formula is C12H22O11. Photosynthesis happens in the chloroplats when energy is absorbed from the sunlight and converted into chemical energy.
This energy is stored temporarily as ATP and NADPH. Next, carbon dioxide and the chemical energy forms organic compunds. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is 6CO2+6H2O light energy C6H12O6+6O2
Source: Pg 114 Modern Biology
#5 Amino Acids
#6 Chloroplast
#7 Matter
#8 Yeast
#9 Periodic table

Alkali metals- They are the most reactive group. When added to water, hydrogen in water is released as a gas and a strong base is formed.
Alkaline earth metals- they become increasingly soluble with a decrease in temperature. This is usually only true in gases.
Carbon family- carbon is the basis of life. It is found in all living material and is an element that is abundant in earths crust.
Transition metals and are earths often acts as catalysts in a reaction.
Source: WWW.learner.org/interactives/periodic/groups10
#10 Chlorophyll

All green plants contain chlorophyll. The 2 main types of chlorophyll are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The allow green light to be reflected or transmitted. This is why plants with a lot of chlorophyll are green. Chlorophyll A is involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll b assist chlorophyll a in capturing light energy.
Source: Pg 115 Modern Biology
#11 Aerobic Respiration

Ferns carry out aerobic respiration because they have chloroplasts. Thy use both respiration and photosynthesis. The steps of aerobic respiration are the following.
First is the Krebs Cycle;
1. two carbon molecules combine with oxaloacetic acid(four-carbon compound) and they make a six-carbon compound known as citric acid. This regenerates co enzyme A.
2.CO2 is released by citric acid and a hydrogen atom. A hydrogen atom forms a five-carbon compound. Citric acid is oxidized and the hydrogen electron reduces NAD+ to NADH.
3. The five-carbon compound releases 1 CO2 and hydrogen atom. Now, a four-carbon compound is produced. NAD+ is released to NADH. ADP becomes ATP.
4.The four carbon compound releases a hydrogen atom to form another four carbon compound. FAD is reduced to FADH2.
5. The four-carbon compound release a hydrogen atom to regenerate oxaloacetic acid which keeps the Krebs cycle going. 10 NADH molecules and two FADH2 molecules that are produced drive the next stage of aerobic respiration. The next stage is Electron Transport chain.
1. NADH and FADH2 give the electron transport chain electrons.
2. Electrons are passed down the chain and they move from molecule to molecule, loosing energy.
3. Lost energy pumps protons and builds a high concentration gradient.
4. This drives the synthesis of ATP. ATP synthase molecules are embedded in the inner membrane and Protons move along the chain and ATP is made from ADP and phosphate.
5. Oxygen accepts electrons and some protons. The protons, electrons and oxygen combine and form water.
Source: PG 139, 156 and 140 Modern Biology
#13 Meiosis



Meiosis produces gametes which are female egg cells or male sperm cells. Meiosis and mitosis are similar in that they have the G-1 phase, S-phase, G-2 phase and they make duplicate cells. Also, DNA coils tightly into chromosomes during prophase. They differ in that meiosis occurs two times before the process is done and meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell. Mitosis makes one identical copy. Meiosis has snyapsis which is where each homologous pair of chromosome in meiosis in a tetrad.
Source:Pg 162, 163 and 156
#14 Baking Soda
#15 Enzyme
#16 Double Helix
#17 Plant life cycle



All plants have a life cycle. The first phase consist of a diploid sporophyte plant that produces spores. The second phase consists of a haploid gametophyte plant that produces sperm and egg. On moss, there are thousands of gametophytes attached to the soil by rhizoids which are like roots. The sporophyte grows up from the top of the gametophyte.
Source: Pg 567 and 565 Modern Biology
#18 Plant without roots
#19 Hypotonic solution
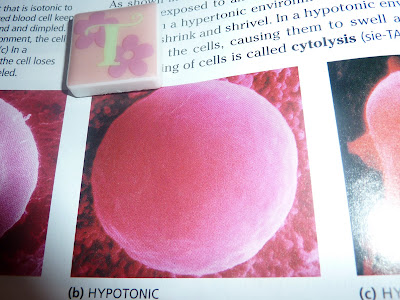
A sulution where water would diffuse into a plant cell is a hypotonic solution because if the concentration of molecules outside the cell are lower than the concentration of molecules in the cell, water will diffuse into the cell until equilibrium is established. Above is a hypotonic cell.
Source: Pg 98 Modern Biology
#22 Hypertonic Solution

A solution in which water would diffuse into a plant cell would be a hypertonic solution because when the concentration of solute molecules outside a cell is higher than inside the cell, water diffuses out of the cell until equilibrium is reached. Above is a cell that is hypertonic to its environment
Source: Pg 100 Modern Biology
#21 Plant like Protists
#22 Animal Protist
#24 Gymnosperm
#25 Angiosperm
#26 Bryophyte
#28 Hypotonic Solution
#29 Amniotic
#30 Fungus
#31 Energy Transformation

Photosynthesis is the transformation of energy from the sun to oxygen. Light from the sun is absorbed in the chloroplast, the organelle where this transformation takes place in a plant and the plant converts the energy to chemical energy. An organism gets energy from eating the plant.
Source: Pg 113 Modern Biology
#32 Double Helix
#33 Cell that can undergo protein synthesis
#34 Archaeabacteria
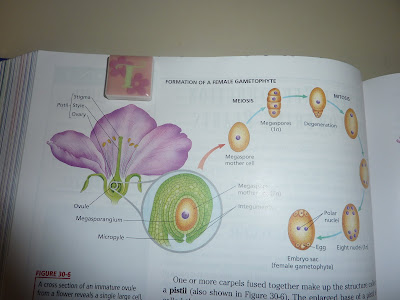
#35 Ovaries of Plant
#36 Living Thing
#37 Deuterostome
#38 Asymmetric
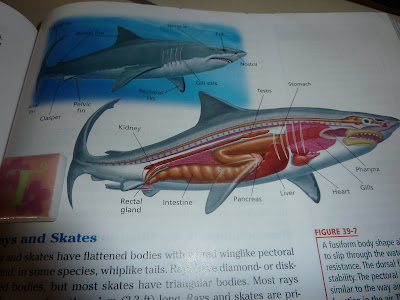
#39 Vertebrates
#40 Protein
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)